Here is more information on this discovery from wikipedia:
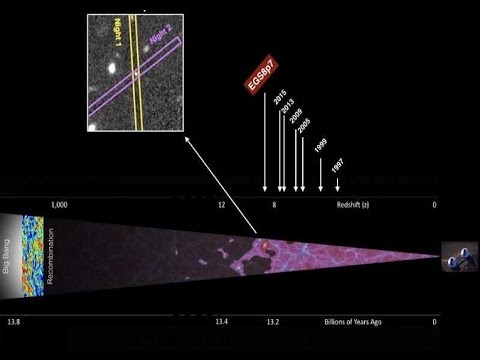
The light of the EGSY8p7 galaxy appears to have been magnified twice during its journey to Earth through gravitational lensing, allowing us to detect such a dim and distant source. In July 2015, EGSY8p7 was announced as the oldest and most-distant known object, surpassing the previously most-distant known galaxy, EGS-zs8-1, which was determined as such in May 2015. EGSY8p7’s distance was determined by measuring the redshift of Lyman-alpha emissions. At the time of EGSY8p7’s announcement it was the most distant known detection of hydrogen’s Lyman-alpha emissions. The distance of this detection is unusual, as neutral hydrogen (atomic hydrogen) clouds in the universe usually absorb these emissions from some even closer sources. The detection indicates large non-uniformity in reionization.
Below are two videos. One is the most recent discovery and one from 2011 where the previous farthest quasar was at 12.9 billion light years.
Note one of the commenters on the video thread makes an astute remark. Not sure if he’s right but it’s a good point:
This all based on the assumption that redshift is an indicator of distance, not age. Yet we are finding close objects that are red shifted and embedded in closer known structures. Redshift has been successfully challenged, standard model science of course ignores it and continues on its merry way. It’s exhausting.
thanks to phys.org for the great info
What ?? How ?